
(See "Rapid sequence intubation for adults outside the operating room", section on 'Placement with proof'.)Ĭapnography uses infrared (IR) radiation to make measurements.

When evaluating studies of EtCO 2, it is essential to distinguish those involving qualitative measurements (colorimetric) from those describing quantitative methods with a graphic waveform display (capnography). An improperly placed ETT in the esophagus will not conduct CO 2 and no change will occur in the color of the litmus paper, which will remain purple. Exhalation of CO 2 from an ETT placed in the trachea will change the color of the litmus paper from purple to yellow.
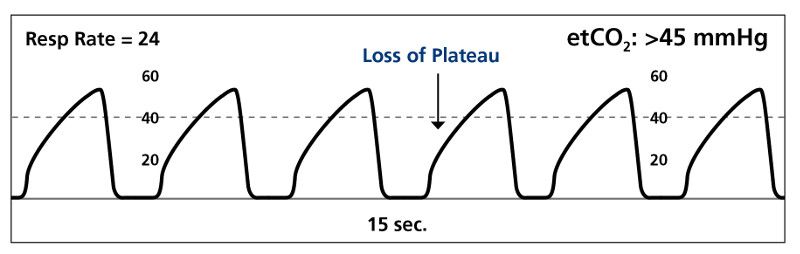
Normal end tidal co2 waveform verification#
Its primary use is for verification of ETT placement. The colorimetric EtCO 2 detector, which consists of a piece of specially treated litmus paper that changes color when exposed to CO 2 (purple for EtCO 2 15 mmHg). Qualitative devices (eg, colorimetric detectors) report the range in which the EtCO 2 falls (eg, 0 to 10 mmHg or >35 mmHg) as opposed to a precise value (eg, 38 mmHg). Quantitative devices measure the precise end-tidal CO 2 (EtCO 2) either as a number (capnometry) or a number and a waveform (capnography). ĬO 2 monitors are either quantitative or qualitative. High-flow systems sampling at ≥100 cc/min have been shown to be inaccurate in neonates, infants, young children, and in hypoventilating adult patients. Low-flow systems are also resistant to dilution from supplemental oxygen.

Low-flow systems have a lower occlusion rate (from moisture or patient secretions) and are accurate in patients with low tidal volumes (eg, neonates, infants, and adult patients with hypoventilation and low tidal volume breathing). Flow rates vary according to the amount of CO 2 needed in the breath sample to obtain an accurate reading. Sidestream systems are configured to use high flow rates (around 150 cc/min) or low flow rates (around 50 cc/min). Sidestream systems are configured for both intubated and nonintubated patients. Mainstream systems are configured for intubated patients. Sidestream devices measure respiratory gas via nasal or nasal-oral cannula by aspirating a small sample from the exhaled breath through the cannula tubing to a sensor located inside the monitor ( picture 1). Mainstream devices measure respiratory gas (in this case CO 2) directly from the airway, with the sensor located on the airway adapter at the hub of the endotracheal tube (ETT). PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION - Carbon dioxide (CO 2) monitors measure gas concentration, or partial pressure, using one of two configurations: mainstream or sidestream. (see "Basic patient monitoring during anesthesia", section on 'Capnography') It is now part of the standard of care for all patients receiving general anesthesia and is part of routine monitoring in the pre-hospital and acute care settings. Capnography provides instantaneous information about ventilation (how effectively CO 2 is being eliminated by the pulmonary system), perfusion (how effectively CO 2 is being transported through the vascular system), and metabolism (how effectively CO 2 is being produced by cellular metabolism).Ĭapnography became a routine part of anesthesia practice in Europe in the 1970s and in the United States in the 1980s. Pulse oximetry provides instantaneous feedback about oxygenation (see "Pulse oximetry"). Oxygenation and ventilation are distinct physiologic functions that must be assessed in both intubated and spontaneously breathing patients. Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. Changes in the shape of the capnogram are diagnostic of disease conditions, while changes in end-tidal CO 2 (EtCO 2), the maximum CO 2 concentration at the end of each tidal breath, can be used to assess disease severity and response to treatment. The relationship of CO 2 concentration to time is graphically represented by the CO 2 waveform, or capnogram ( figure 1). INTRODUCTION - This topic review will discuss the basic physiology and interpretation of capnography and its use in emergency settings.ĭEFINITION AND BACKGROUND - The term capnography refers to the noninvasive measurement of the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO 2) in exhaled breath expressed as the CO 2 concentration over time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
